Hello All!
I have a requirement to purge the older data from the tables that are marked with soft delete for now. The tables are related by the key column - GROUP_ID at the top end of the hierarchy.
I am using the 12c version 12.1.0.2 that is yet and planned to go through the Proactive bundle patch Jan 2018. It is a standalone and Non-CDB server.
SQL> select * from v$version;
BANNER CON_ID
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
Oracle Database 12c Enterprise Edition Release 12.1.0.2.0 - 64bit Production 0
PL/SQL Release 12.1.0.2.0 - Production 0
CORE 12.1.0.2.0 Production 0
TNS for Linux: Version 12.1.0.2.0 - Production 0
NLSRTL Version 12.1.0.2.0 - Production 0
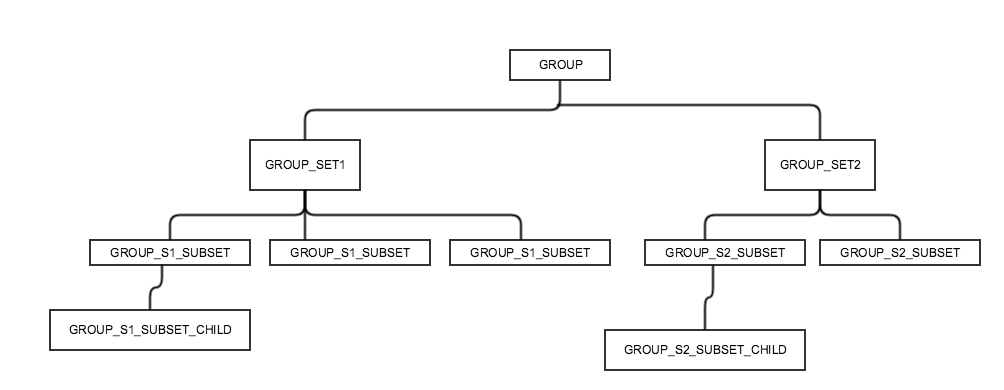
The below image shows a sample hierarchy of the tables. GROUP_SET1 and GROUP_SET2 have foreign key for ID from GROUP table. The ID column is the Primary Key for the table - GROUP. The other child tables like SUBSET and SUBSET_CHILD are related by IDs from the parent tables. There are about 70 tables in that hierarchy in total and the major contributor would be like GROUP_S1_SUBSET in that diagram for like 40+ tables.
The approach that I am thinking to try out is that the table - GROUP would be list or interval partitioned for the ID column. All other tables would be REFERENCE partitioned based on the IDs so that the purge could be performed like below.
ALTER TABLE group TRUNCATE PARTITION set1 CASCADE UPDATE INDEXES;
However the concerns are as below.
- Oracle states that the max # of partitions allowed per table/index is 1024K - 1. The master table - GROUP currently has 4000 records now and it would be partitioned for every record to achieve this REF partitioning. The table is expected to grow more in thousands.
- Has anyone implemented a table with more than 10K partitions and faced no or any issues?
- Would you recommend any checks before partitioning an object with such # of partitions?
- As the tables are REF partitioned, would there be any considerable performance impact with the DMLs? The reference partitioning key column would not be updated to avoid any row migration but the other attributes of the record could be updated and majority of the DMLs would be INSERTs based on JOINs from multiple tables (INSERT..SELECT).