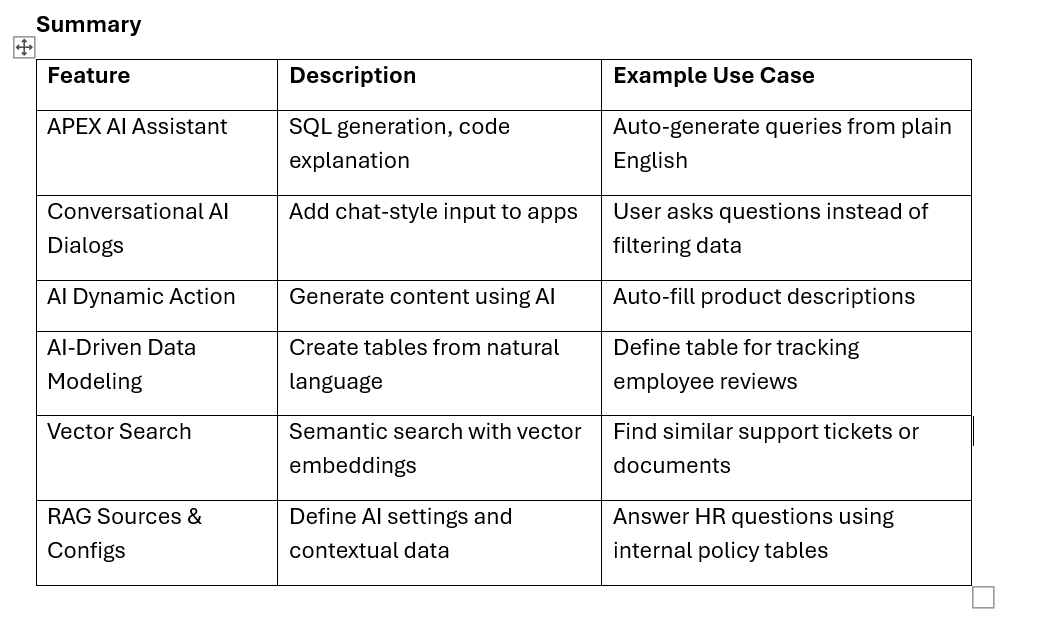
Oracle APEX now includes cutting-edge Generative AI and Natural Language Processing (NLP) capabilities to simplify development and enhance user experience. Here's an overview with real-world examples and code snippets:
1. APEX AI Assistant
Example 1: SQL Generation from Natural Language
Prompt:
"Show all employees in department 10 who joined after Jan 1, 2020"
AI Assistant Output (SQL):
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, hire_date
FROM employees
WHERE department_id = 10
AND hire_date > TO_DATE('2020-01-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD');
🛠️ Example 2: Code Debugging / Explanation
Input (PL/SQL):
BEGIN
UPDATE employees SET salary = salary * 1.10 WHERE department_id = 20;
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN
NULL;
END;
AI Assistant Feedback:
"The WHEN OTHERS THEN NULL block silently swallows all errors. Consider logging the error or handling it explicitly."
2. Conversational AI Dialogs
Enables chatbot-like interactions directly in your app UI.
💬 Example: Add Conversational Search
Use the Conversational Dialog page component to allow queries like:
User Input:
"List top 5 highest-paid employees in Sales"
Dynamic Query Built by APEX:
SELECT * FROM (
SELECT first_name, last_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE department_name = 'Sales'
ORDER BY salary DESC
)
WHERE ROWNUM <= 5;
Setup: Use the Conversational Dialog region and bind it to a RESTful service or custom PL/SQL logic for query execution.
3. Generate Text with AI Dynamic Action
A new dynamic action to generate content on the fly.
Example: Auto-Generate Product Descriptions
PL/SQL Code in Dynamic Action:
DECLARE
l_output CLOB;
BEGIN
l_output := apex_ai.generate_text(
p\_prompt => 'Write a short marketing description for a ' || :P1\_PRODUCT\_NAME,
p\_temperature => 0.7
);
:P1_DESCRIPTION := l_output;
END;
Result:
When user enters “Smart LED Bulb”, the system populates:
“A sleek, energy-efficient LED bulb with smart home compatibility and customizable brightness.”
4. AI-Driven Data Modeling
Generate full table scripts from plain English descriptions.
Example: Create Table via SQL Workshop Prompt
Prompt:
“Create a table for tracking customer feedback with customer name, feedback text, rating (1-5), and submission date.”
Generated SQL:
CREATE TABLE customer_feedback (
feedback_id NUMBER GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
customer_name VARCHAR2(100),
feedback_text CLOB,
rating NUMBER CHECK (rating BETWEEN 1 AND 5),
submission_date DATE DEFAULT SYSDATE
);
Also available in Quick SQL format for rapid prototyping.
5. Vector Search Support
Leverage semantic search with Oracle Database 23ai integration.
Example: Search for Similar Support Tickets
Vector Embedding SQL Example:
SELECT ticket_id, title, similarity_score
FROM support_tickets
ORDER BY VECTOR_SIMILARITY(embedding, apex_ai.embed_text(:P1_QUERY)) DESC
FETCH FIRST 5 ROWS ONLY;
User Query:
"Issue with login timeout"
Result:
Returns semantically similar tickets like:
- "User gets logged out after 5 minutes"
- "Session expired unexpectedly"
6. AI Configurations & RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) Sources
Centralize and manage your AI prompts, services, and data sources.
Example: Define a RAG Source for HR Policy Lookup
SQL Source for RAG (Shared Component):
SELECT section_title, section_content
FROM hr_policies
WHERE LOWER(section_content) LIKE '%' || LOWER(:input) || '%';
Prompt Template:
“Based on the HR policy, answer the user's question using only this content: {rag_result}”
PL/SQL to Generate Answer:
:P1_AI_ANSWER := apex_ai.generate_text(
p_prompt => apex_ai.get_rag_prompt(
p\_source\_name => 'HR\_POLICY\_SOURCE',
p\_input => :P1\_USER\_QUESTION
)
);
User Input:
“What’s our maternity leave policy?”
AI Response:
“According to company policy, employees are entitled to 16 weeks of paid maternity leave, with an option to extend unpaid leave by 4 weeks.”